The term topology
refers to the way a network is laid out, either physically or logically. Physical topology refers to the
placement of the network's various components, including device location and
cable installation, while logical topology shows how data flows within a network, regardless of its
physical design. We will briefly discuss various topologies of LAN.
Previous : Network Technologies Based on Scale
Bus Topology
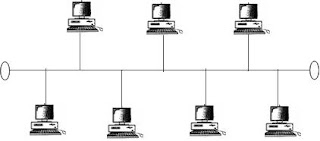
Bus
topology is an implementation of broadcast networks. In bus topology, a single
long cable acts as a backbone to link all devices in the network.
Advantages
·
Ease of installation
·
Cheap and simple
·
Uses less cables
Disadvantages
·
Difficulty in fault tolerance and reconfiguration.
·
A break in the cable stops all transmissions.
Ring Topology
In ring topology, each node has a dedicated
point-to-point connection only with the two nodes in either side of it. A
message or signal is passed along the ring in one direction, from device to
device, until it reaches its destination.
 |
| Ring Topology |
Advantages
·
Easy to install and reconfigure
·
Fault isolation is simplified
·
Perform better than bus topology under heavy load
Disadvantages
·
Unidirectional traffic
·
A break in the ring can disable the entire network
Star Topology
Star networks are the most common LAN
topology. In a star topology, each device has a dedicated link inly to a
central controller, usually the hub. All data exchange between devices take
place through hub.
 |
| Star topology |
Advantages
·
Better performance
·
Isolation of devices
·
Benefits from centralization
Disadvantage
of the star topology is that if the
central controller fails, the entire network goes down with it.
No comments:
Post a Comment