Based on the transmission technology
computer networks are classified into two.
1. Broadcast Networks
2. Point-to-Point networks
Broadcast Networks
Broadcast network have a communication channel that is
share by all the nodes in the network. BUS network is an example of broadcast
network.
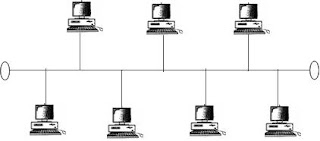 |
| BUS network |
All
the nodes on the network receive the messages sent by any machine in broadcast
network. An address field of the message determines the intended recipient.
Upon receiving a message, the node checks the address field of the message. If
the message is intend to itself then process the packet otherwise it simply
ignore the packet.
Broadcasting refers to a method of
transferring a message to all recipients simultaneously. Some broadcast system
also support multicasting. Multicasting
means send data to a subset of nodes in the network.
 |
| Broadcasting |
 |
| Multicasting |
Point-to-point Networks
In the
case of point-to-point network, there exist many connections between individual
pairs of nodes. A transmitted packet may visit some intermediate node before
they actually reach its destination. There may multiple routes between two
nodes so routing algorithms play an important rule in point to point networks.
The
connection between two nodes either one of the following
1.
Dedicated
2.
Shared
In the
case of dedicated connection, there exist a dedicated connection between sender
and receiver. Three types of dedicated connections are there
a.
simplex
b.
half duplex
c.
duplex
Simplex connections only allow
the transmission of data in one direction. Radio and TV are examples. In contrast, links that can be used
in either direction, but only one way at a time, like a single-track railroad
line are called half-duplex links. CBZ radio is a half-duplex device.
Links that can be use in both directions at the same time, like a two-lane
road, are call full-duplex links. Point-to-point transmission with one sender and one receiver
is sometimes call unicasting.
Shared devices
share the transmission link by using the technique known as multiplexing, we
will discuss multiplexing later.
Previous : Computer Networks Definition and History
No comments:
Post a Comment