Asynchronous transfer mode is an International Telecommunication
union- Telecommunication section (ITU-T)
standard for cell relay. Wherein information
for multiple service types such as video, voice or data is conveyed in small
fixed size cells. A cell network uses the cell as the basic unit of data
exchange. A cell is defined as a small, fixed-size block of information.
Index : Computer Networks and Communication online coaching
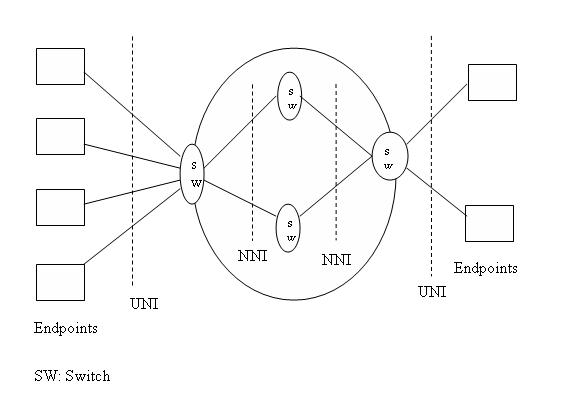
ATM Network Interfaces
An ATM network of a set of ATM switches interconnected
by point-to-point ATM links or interfaces. ATM switche support two primary
types of interfaces: UNI and NNI.UNI(User Network Interface) connects ATM end
systm to an ATM switch. NNI(Network-Network Interface) connects two ATM
switches. Connection between two
endpoints is accomplished through transmission paths (TPs), virtual paths
(YPs), and virtual circuits (YCs). Architecture of an ATM network
shown below,
 |
| Architecture of an ATM network |
Cells
The
basic data unit in an ATM network is called a cell. A cell is only 53 bytes
long with
5 bytes allocated to the header and 48 bytes carrying the
payload, user data may be less than 48 byte.
 |
| ATM Cell |
ATM Layers
ATM
standard consist three layers. They are, the application adaptation layer (AAL),
the ATM layer, and the physical layer. The endpoints use all layers but, the
switches use only the two bottom layers.
 |
| ATM Layers |
Physical Layer
The Physical Layer is responsible for the electrical
or optical transmission and receipt along the physical media between two
devices.
ATM Layer
The ATM layer provides routing, traffic management,
switching, and multiplexing services. Other functions are,
- Cell header generation/extraction.
- Multiplexing and de-multiplexing of cells.
- Managing of cell flow and sequencing.
- Handling dropped cells.
- Switch-based routing using virtual paths and virtual
circuits.
ATM Adaptation Layer
The
main services provided by AAL (ATM Adaptation Layer) are:
Segmentation and reassembly, handling of transmission
errors, handling of lost cell conditions, timing and flow control
Next : Questions
Index : Computer Networks and Communication online coaching
No comments:
Post a Comment