Here
we discuss some modern ciphers, modern ciphers are bit oriented. Some simple
modern ciphers are XOR, Rotation, Substitution cipher (s-box), Permutation
cipher (p-box).
XOR Cipher
XOR
ciphers use logical XOR operation to produce ciphertext. Two inputs are needed
for XOR cipher algorithm, one input from plaintext and other input is the key
to encrypt. The inputs are just XORed to produce ciphertext.
Rotation Cipher
Rotation
ciphers rotate the bits in the input plaintext to produce the ciphertext. Rotation
ciphers can be either keyed or keyless. The number of rotation must be in
between 1 to N-1 for an N bit input. After Nth rotation, we get the original
string.
Substitution cipher: S-box
It is
a parallel version of traditional substitution cipher. The input to an S-box is
a group of bits with length N and the output is another group of bits with
length M (M and N need not to same).
Transposition Cipher: P-box
The P-box (permutation box), produce cipher text by
transposition at bit level in input string. There exist three types of P-box
ciphers: the straight
permutation, expansion permutation, and
compression permutation.
In straight P-box, the number of inputs and
outputs are same.
In expansion P-box, number of outputs is
greater than number of inputs.
In compression P-box cipher number of outputs
are smaller than number of inputs.
Modern Ciphers
Modern Ciphers
Here
we discuss some modern ciphers, modern ciphers are bit oriented. Some simple
modern ciphers are XOR, Rotation, Substitution cipher (s-box), Permutation
cipher (p-box).
 |
| P-Boxes |
Modern
ciphers are some times called round ciphers, because they contain multiple
rounds operations for encryption and decryption. DES and AES are two modern
symmetric ciphers. Both AES and DES divide plaintext to different blocks and
use same key for encrypt and decrypt the blocks.
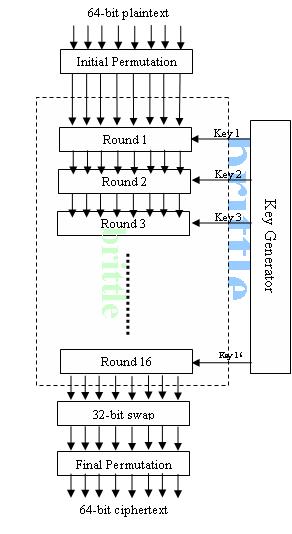
Data Encryption Standard (DES)
DES was
originally designed by IBM and adopted by US government for secure exchange of
data. The algorithm divides the plaintext to 64-bit blocks and produce 64-bit
ciphertext for each block. Outline of DES is shown below;
 |
| DES |
DES use two transposition blocks (p-box), {they are
straight and inverse of each other and keyless}, 16 round ciphers (each round
use different keys derived from original key), and the stage prior to the final
permutation, exchanges the leftmost 32 bits with the rightmost 32 bits.
The following
figure shows on round in DES.
 |
| DES Encryption |
The
DES function apply 48-bit key (Ki) to right most 32-bits of the input (Ri) to
produce 32-bit output. This function contains four operations: an XOR
operation, an expansion permutation, a group of s-boxes and a straight
permutation as shown below,
 |
| DES function |
Next : RSA
Previous : Cryptography
No comments:
Post a Comment